Hovering over an image will enlarge it and point out features (works better on desktop than on mobile).
![]() A camera indicates there are pictures.
A camera indicates there are pictures.
![]() A speaker indicates that a botanical name is pronounced.
A speaker indicates that a botanical name is pronounced.
![]() A plus sign after a Latin name indicates that the species is further divided into varieties or subspecies.
A plus sign after a Latin name indicates that the species is further divided into varieties or subspecies.
Most habitat and range descriptions were obtained from Weakley's Flora.
Your search found 2 taxa in the family Aizoaceae, Carpetweed family, as understood by PLANTS National Database.
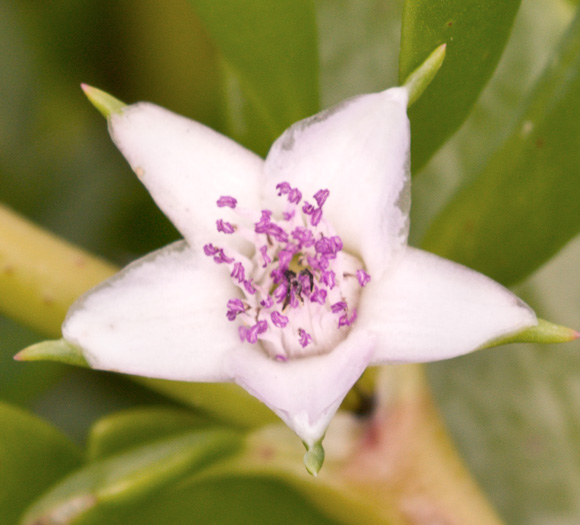
![]() Common Name:
Large Sea-purslane, Shoreline Sea-purslane
Common Name:
Large Sea-purslane, Shoreline Sea-purslane
Weakley's Flora: (4/24/22) Sesuvium portulacastrum FAMILY: Aizoaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH PLANTS National Database: Sesuvium portulacastrum FAMILY: Aizoaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH Vascular Flora of the Carolinas (Radford, Ahles, & Bell, 1968): Sesuvium portulacastrum 069-01-001 FAMILY: Aizoaceae
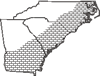
Habitat: Island end sand flats and sea beaches; less typically inland (LA) in saline marshes or seeps (associated with salt domes)
Uncommon in Coastal Plain of GA & SC, rare in NC
Native to the Carolinas & Georgia

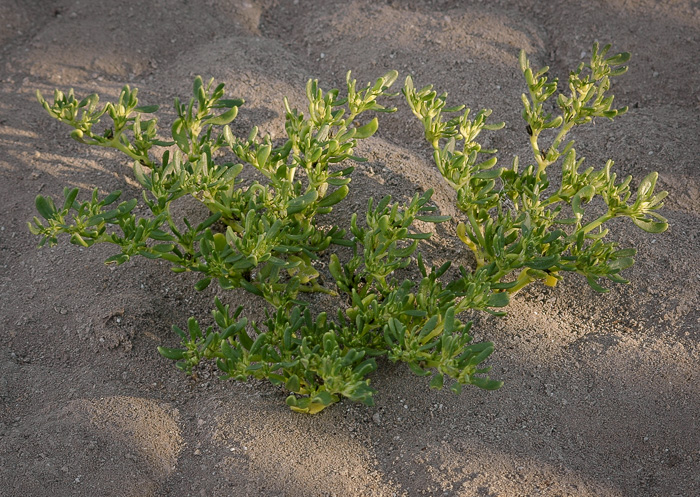
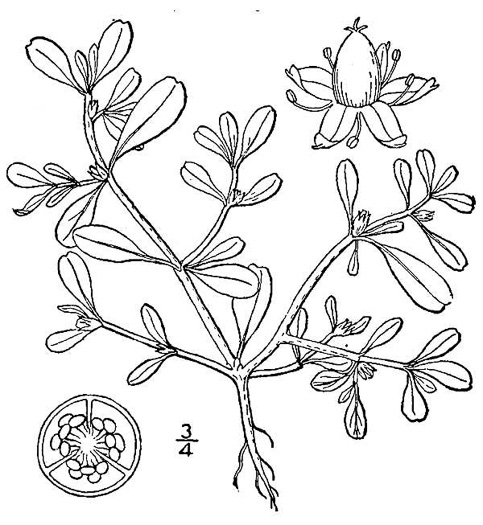
![]() Common Name:
Small Sea-purslane, Slender Sea-purslane
Common Name:
Small Sea-purslane, Slender Sea-purslane
Weakley's Flora: (4/24/22) Sesuvium maritimum FAMILY: Aizoaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH PLANTS National Database: Sesuvium maritimum FAMILY: Aizoaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH Vascular Flora of the Carolinas (Radford, Ahles, & Bell, 1968): Sesuvium maritimum 069-01-002 FAMILY: Aizoaceae
Habitat: Island end flats and sea beaches, salt flats; less typically inland (AL, LA) in saline marshes or seeps (associated with salt domes)
Uncommon in Coastal Plain
Native to the Carolinas & Georgia
Your search found 2 taxa. You are on page PAGE 1 out of 1 pages.